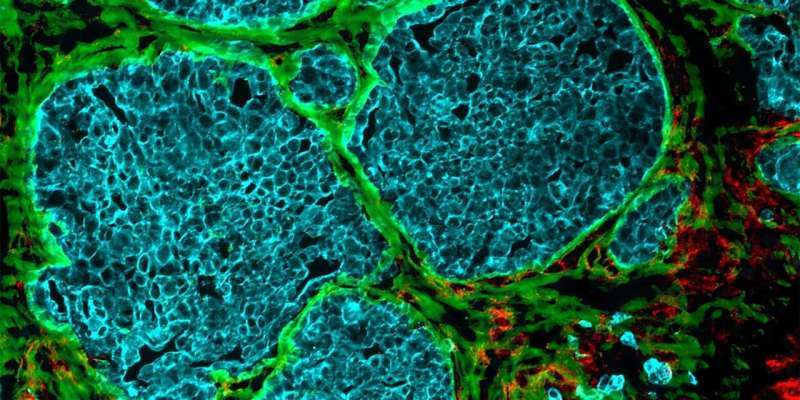
An increasing number of dense cellular clusters in rising tumors convert blood vessels into fiber-filled channels. This makes immune cells much less efficient, as findings through researchers from ETH Zurich and the College of Strasbourg counsel. Their analysis is revealed in Matrix Biology.
It used to be nearly ten years in the past that researchers first noticed that tumors going on in numerous cancers—together with colorectal most cancers, breast most cancers and melanoma—show off channels main from the outside to the interior of the cellular cluster. However how those channels shape, and what purposes they carry out, lengthy remained a thriller.
Contents
Elaborate and detailed experiments
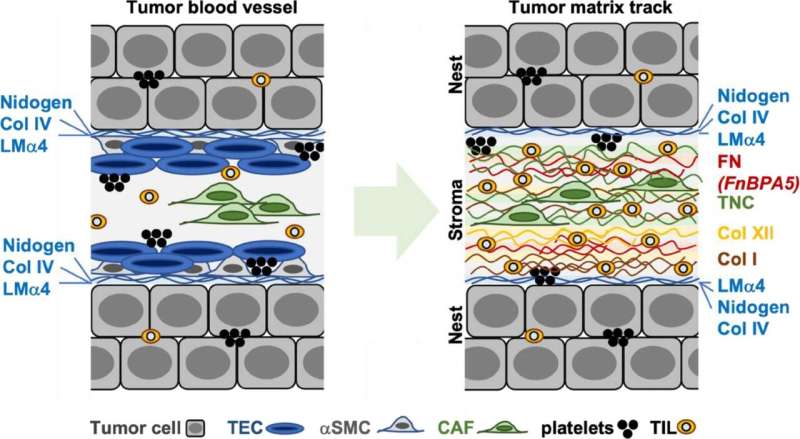
Thru a chain of elaborate and detailed experiments, the analysis teams led through Viola Vogel, Professor of Carried out Mechanobiology at ETH Zurich, and Gertraud Orend from the College of Strasbourg have discovered imaginable solutions to those questions. There may be a substantial amount of proof to signify that those channels, which the researchers have dubbed tumor tracks, had been as soon as blood vessels.
Those blood vessels get started out through supplying the fast-growing cellular clusters with glucose and oxygen. However then the vessels go through a procedure that strips them in their unique serve as of transporting blood: the vessel partitions trade and the vessel hollow space step by step fills up.
When fibers keep an eye on the conduct of immune cells
This filler subject matter is composed principally of cells and newly shaped protein fibers, which make up what’s referred to as the extracellular matrix. Collagen fibers are discovered right here, as are fibronectin fibers. The latter play a job in expansion processes that happen principally all through embryonic building or wound therapeutic. Of their article, the researchers display that the fibers inside the tumor tracks are in a position to trapping immune cells.
Whilst this occurs, the immune cells stretch out alongside the channels and stick with the unfastened fibronectin fibers. “On this elongated shape, the immune cells transfer from combating sicknesses to supporting therapeutic processes,” Vogel says. As an alternative of attacking the tumor cells, they excrete molecules that stimulate expansion, thus serving to the most cancers cells to multiply.
The up to now unknown position of tissue stress
It turns into transparent that the stress of extracellular matrix fibers performs a key and up to now unknown position in tumor building: in wholesome tissue, the fibronectin fibers are stretched extraordinarily taut; most effective in tumor tissue are they slack. On this looser, extra comfy shape, surrounded through reworked blood vessel partitions, the fibronectin fibers it appears that evidently create a recess through which most cancers cells can develop undisturbed.
Vogel says that the principle center of attention of most cancers analysis has been at the cells: “The extracellular matrix used to be steadily lost sight of.” That is why the crosstalk between cells and their surroundings nonetheless stays a thriller. “However if you wish to perceive what a spider does, you even have to have a look at its internet,” she says.
Investigating tissue samples from sufferers
Vogel due to this fact additionally sees the brand new findings as a explanation why to enlarge her analysis center of attention and acquire a greater working out of the larger image. “The simpler we know how the microenvironment steers how tumor cells multiply, the likelier it’s that we’re going to have the option of stopping them from doing so,” she says.
Vogel does, on the other hand, cautions to translate the consequences of the effects to people as a result of they’re in response to experiments on mice with breast most cancers. It is still observed whether or not or no longer those effects may also be carried out immediately to cancers in people. However there are certainly a number of parallels, as Orend’s team exterior lately demonstrated.
In the meantime, Vogel’s analysis team has began participating with the Kantonsspital Baden on a follow-up mission: one among Vogel’s doctoral scholars is investigating if tissue samples taken from breast most cancers sufferers additionally comprise lines of transformed blood vessels. “We are curious to find the place we’re going to in finding similarities and the place we’re going to see variations,” Vogel says.
Additional info:
Charlotte M. Fonta et al, Infiltrating CD8+ T cells and M2 macrophages are retained in tumor matrix tracks enriched in low stress fibronectin fibers, Matrix Biology (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.matbio.2023.01.002
Devadarssen Murdamoothoo et al, Tenascin‐C immobilizes infiltrating T lymphocytes via CXCL12 selling breast most cancers development, EMBO Molecular Medication (2021). DOI: 10.15252/emmm.202013270
Quotation:
How tumors become blood vessels (2023, March 17)
retrieved 4 April 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-03-tumors-blood-vessels.html
This record is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal learn about or analysis, no
phase could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is equipped for info functions most effective.
Supply Through https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-03-tumors-blood-vessels.html