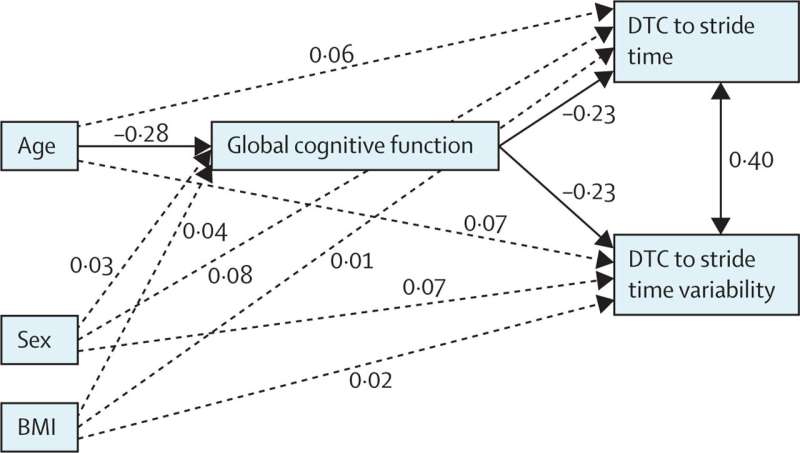
Most cancers remedies have lengthy been shifting towards personalization—discovering the fitting pills that paintings for a affected person’s distinctive tumor, in accordance with particular genetic and molecular patterns. Many of those centered treatments are extremely efficient, however are not to be had for all cancers, together with non-small mobile lung cancers (NSCLCs) that experience an LKB1 genetic mutation.
A brand new learn about led by means of Salk Institute Professor Reuben Shaw and previous postdoctoral fellow Lillian Eichner, now an assistant professor at Northwestern College, published FDA-approved trametinib and entinostat (which is recently in medical trials) may also be given in tandem to provide fewer and smaller tumors in mice with LKB1-mutated NSCLC.
The findings have been printed in Science Advances on March 17, 2023.
“For non-small mobile lung most cancers instances with the LKB1 mutation, usual chemotherapy and immunotherapy remedies aren’t efficient,” says Shaw, senior and co-corresponding creator of the learn about, and director of Salk’s Most cancers Heart. “Our findings show there’s a strategy to goal those instances the usage of pills which might be FDA-approved or already in medical trials, so this paintings may just simply be used for a medical trial in people.”
Kind of 20 % of all NSCLCs have the LKB1 genetic mutation, because of this there aren’t any efficient centered treatments recently available on the market for sufferers with this most cancers kind. To create a treatment that would goal the LKB1 mutation, the researchers became to histone deacetylases (HDACs). HDACs are proteins related to tumor enlargement and most cancers metastasis, with function overexpression in forged tumors.
A number of HDAC-inhibitor pills are already FDA-approved (secure for human use) for particular kinds of lymphoma, however knowledge on their efficacy in forged tumors or whether or not tumors bearing particular genetic alterations might show off heightened healing attainable has been missing.
In accordance with earlier findings connecting the LKB1 gene to 3 different HDACs that every one depend on HDAC3, the staff began by means of carrying out a genetic research of HDAC3 in mouse fashions of NSCLC, finding an rapidly essential function for HDAC3 in more than one fashions. After organising that HDAC3 was once essential for the expansion of the difficult-to-treat LKB1-mutant tumors, the researchers subsequent tested whether or not pharmacologically blockading HDAC3 may just give a in a similar fashion potent impact.
The staff was once serious about trying out two pills, entinostat (an HDAC inhibitor in medical trials identified to focus on HDAC1 and HDAC3) and FDA-approved trametinib (an inhibitor for a distinct elegance of enzymes associated with most cancers). Tumors frequently turn into temporarily immune to trametinib, however co-treatment with a drug that inhibits a protein downstream of HDAC3 is helping cut back this resistance.
As a result of that protein is dependent upon HDAC3, the researchers believed {that a} drug that objectives HDAC3—like entinostat—would lend a hand organize trametinib resistance, too.
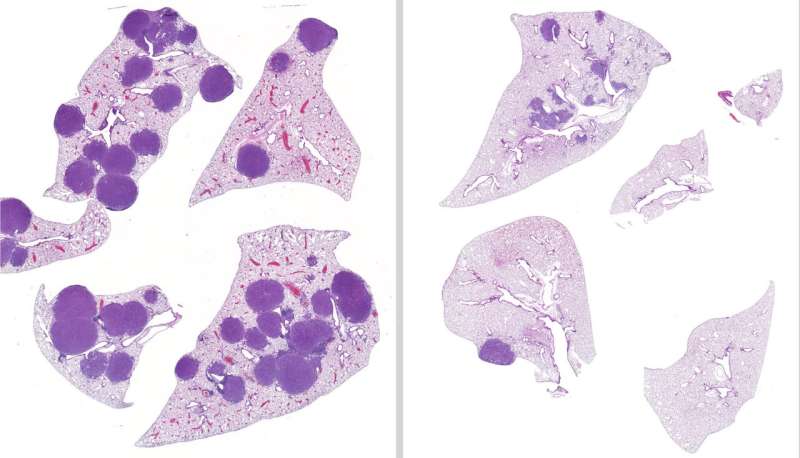
After treating mice with LKB1-mutated lung most cancers with variable remedy regimens for 42 days, the staff discovered that mice given each entinostat and trametinib had 79 % much less tumor quantity and 63 % fewer tumors of their lungs than the untreated mice. Moreover, the staff showed that entinostat was once a viable remedy possibility in instances the place a tumor was once immune to trametinib.
“We idea the entire HDAC enzyme elegance was once immediately connected to the reason for LKB1 mutant lung most cancers. However we did not know the precise function of HDAC3 in lung tumor enlargement,” says first and co-corresponding creator Eichner. “We’ve got now proven that HDAC3 is very important in lung most cancers, and that this is a druggable vulnerability in healing resistance.”
The findings might result in medical trials to check the brand new routine in people, since entinostat is already in medical trials and trametinib is FDA-approved. Importantly, Shaw sees this discovery as transformative for cancers past NSCLC, with attainable packages in lymphoma, melanoma, and pancreatic most cancers.
“Our lab has dedicated years to this mission, taking small and significant steps towards those findings,” says Shaw, holder of the William R. Brody Chair. “That is in reality a good fortune tale for a way elementary discovery science can result in healing answers within the not-so-distant long run.”
“My unbiased laboratory is lucky to be a part of the Lurie Most cancers Heart on the Feinberg College of Drugs at Northwestern College, which could be very supportive of translational analysis. We are hoping that this setting will facilitate the initiation of a medical trial in accordance with those findings,” says Eichner.
Additional information:
Lillian Eichner et al, HDAC3 is important in tumor building and healing resistance in Kras-mutant non–small mobile lung most cancers, Science Advances (2023). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.add3243. www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.add3243
Quotation:
New mixture of substances works in combination to cut back lung tumors in mice (2023, March 17)
retrieved 23 March 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-03-combination-drugs-lung-tumors-mice.html
This file is topic to copyright. Except any truthful dealing for the aim of personal learn about or analysis, no
section is also reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions most effective.
Supply Via https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-03-combination-drugs-lung-tumors-mice.html